Split phase inverter vs single phase inverter
- 12/29/2023
Understanding Split Phase and Single Phase Inverters: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
In today’s interconnected world, electrical power is the lifeblood that fuels our homes, businesses, and industries. As we seek efficient and reliable ways to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), inverters play a pivotal role. Among the various types of inverters, split phase and single phase variants stand out for their unique characteristics and applications.
1. Split Phase Inverters
1.1 What Are Split Phase Inverters?
A split phase inverter is a versatile device that transforms DC power (often from solar panels or batteries) into 120V and 240V AC power. It’s commonly used in residential and light commercial settings where dual voltage levels are essential. Let’s break down its key features:
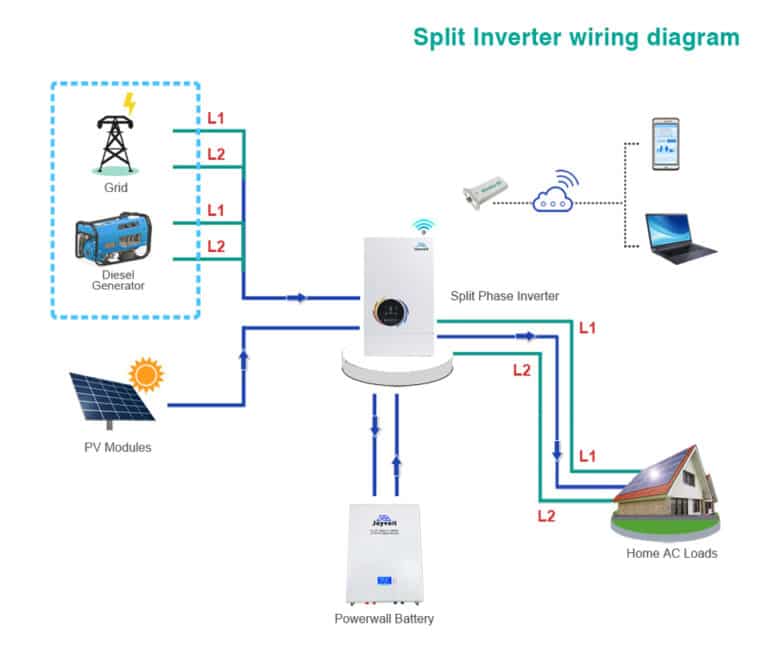
- Dual Output Wires (L1 and L2):The split phase inverter boasts two output wires—L1 and L2. These wires are intentionally 180 degrees out of phase with each other. When combined, they create a 240V potential difference.
- Neutral Wire (N):The neutral wire connects to the center tap of the transformer. The voltage between L1 (or L2) and neutral is 120V, making it suitable for standard household appliances.
1.2 Applications of Split Phase Inverters
- Residential Power Backup:During power outages, split phase inverters can seamlessly switch to battery power, ensuring essential appliances like refrigerators, lights, and computers remain operational.
- RVs and Mobile Homes:Split phase inverters provide both 120V and 240V power, making them ideal for mobile living spaces.
- Light Commercial Use:Small businesses, workshops, and remote offices benefit from split phase inverters, especially when 240V equipment (such as power tools) is necessary.
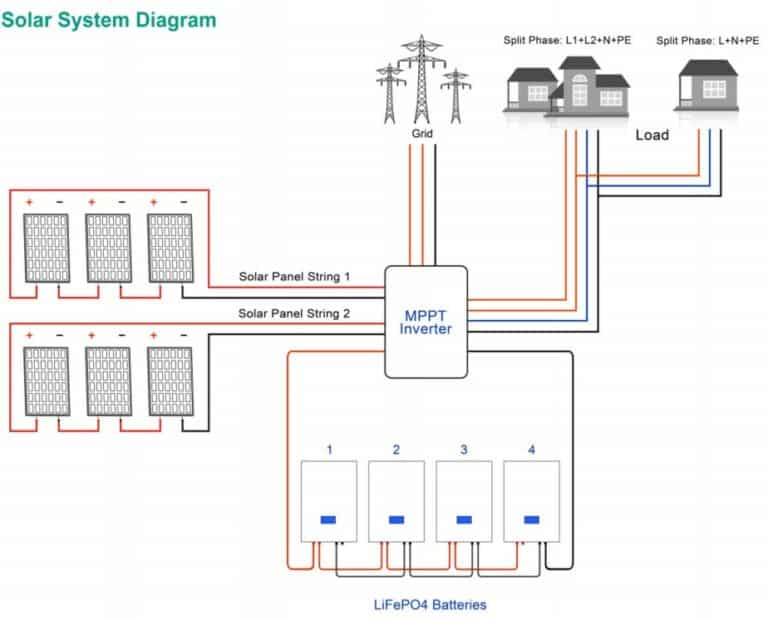
2. Single Phase Inverters
2.1 Unveiling Single Phase Inverters
A single phase inverter simplifies the equation by offering either 120V or 240V AC output. Here’s what you need to know:
- Single Output Wire (L):The single phase inverter has only one output wire (L), which aligns with the neutral wire. Depending on the configuration, it delivers either 120V or 240V AC power.
2.2 Where Are Single Phase Inverters Used?
- Home Solar Systems:Single phase inverters are prevalent in residential solar installations, converting DC energy from solar panels into usable AC power.
- Small Appliances and Electronics: Devices like laptops, TVs, and phone chargers operate on 120V AC, making single phase inverters suitable for low to moderate power loads.
3. Key Differences
3.1 Input Power Configuration
- Split Phase:Accepts a single DC input and generates dual AC voltages (120V and 240V).
- Single Phase:Also accepts a single DC input but provides only one AC voltage level (either 120V or 240V).
3.2 Output Voltage Levels
- Split Phase:Offers both 120V and 240V power sources.
- Single Phase:Provides a single voltage level (either 120V or 240V).
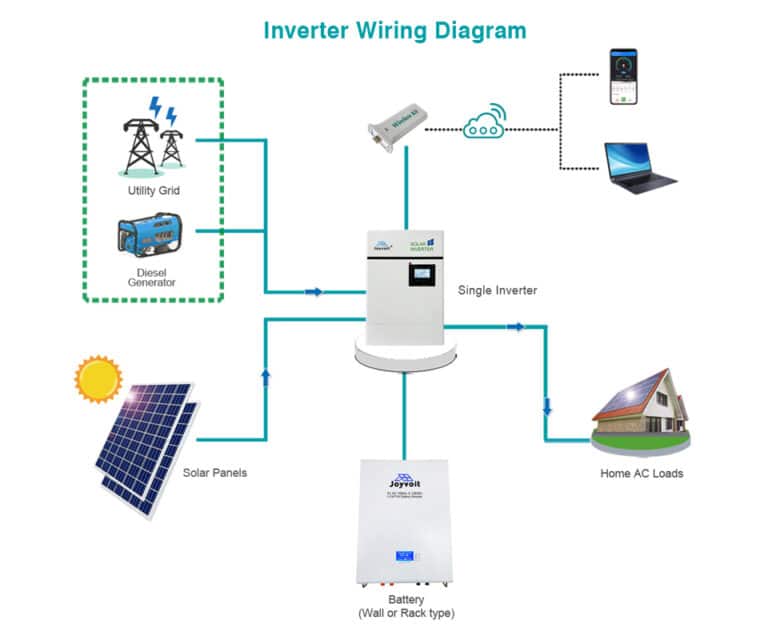
Conclusion
Inverters bridge the gap between DC and AC power, enabling us to harness electricity efficiently. Whether you’re powering your home, charging your electric vehicle, or running a small business, understanding the nuances of split phase and single phase inverters empowers you to make informed decisions.
Remember, the next time you flip a switch or plug in a device, there’s an inverter silently at work, transforming energy to meet our modern needs.
Understanding Three-Phase Inverters: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Three-Phase Inverters
In the realm of electrical power conversion, three-phase inverters play a pivotal role. These electronic devices accept direct current (DC) input and transform it into three-phase alternating current (AC) output. Here’s what you need to know:
1.What Is a Three-Phase Inverter?
- A three-phase inverter is essential for converting DC voltage to three-phase AC supply.
- It finds applications in high-power systems, such as industrial motors and residential power grids where three-phase AC power is standard.
2.How Does a Three-Phase Inverter Work?
- Imagine three arms, each delayed by 120 degrees, working together to produce a three-phase AC supply.
- The inverter switches operate in a synchronized manner, creating a line-to-line output waveform with six steps.
- By applying pulse width modulation (PWM) techniques, the waveform’s basic shape is refined, canceling out unwanted harmonics.
3.Applications of Three-Phase Inverters:
- Industrial Machinery:Three-phase inverters drive motors, pumps, and compressors in factories and manufacturing plants.
- Renewable Energy Systems:They convert DC power from solar panels or wind turbines into grid-compatible AC power.
- HVAC Systems:Three-phase inverters efficiently control heating, ventilation, and air conditioning units.
- Electric Vehicles:Inverters play a crucial role in electric vehicle propulsion systems.
Choosing the Right Inverter: Key Considerations
1.Power Requirements:
- Accurately assess your home’s power needs. Consider wattage ratings, start-up surge watts (peak wattage), and voltage requirements.
- Calculate the maximum continuous wattage load to determine the inverter’s capacity.
2.Efficiency and Size:
- Look for an inverter that balances efficiency with size. Larger inverters may be more efficient but require a bigger battery bank.
- Consider available installation space and portability.
3.Type of Load:
- Resistive loads (e.g., lights, heaters) have straightforward power requirements.
- Inductive loads (e.g., motors, compressors) have higher start-up surge demands.
4.Waveform Quality:
- Pure sine wave inverters provide clean power similar to utility grid electricity.
- Modified sine wave inverters are more affordable but may not be suitable for sensitive electronics.
5.Battery Compatibility:
- Ensure the inverter is compatible with your battery bank (if using one).
- Consider battery capacity and maintenance requirements.

Conclusion
According to Wikipedia, some of the countries that use a split phase power system are:
United States
Canada
Mexico
Brazil
Colombia
Venezuela
Philippines
Some of the countries that use a single phase power system are:
United Kingdom
France
Germany
Spain
Italy
China
India
Australia
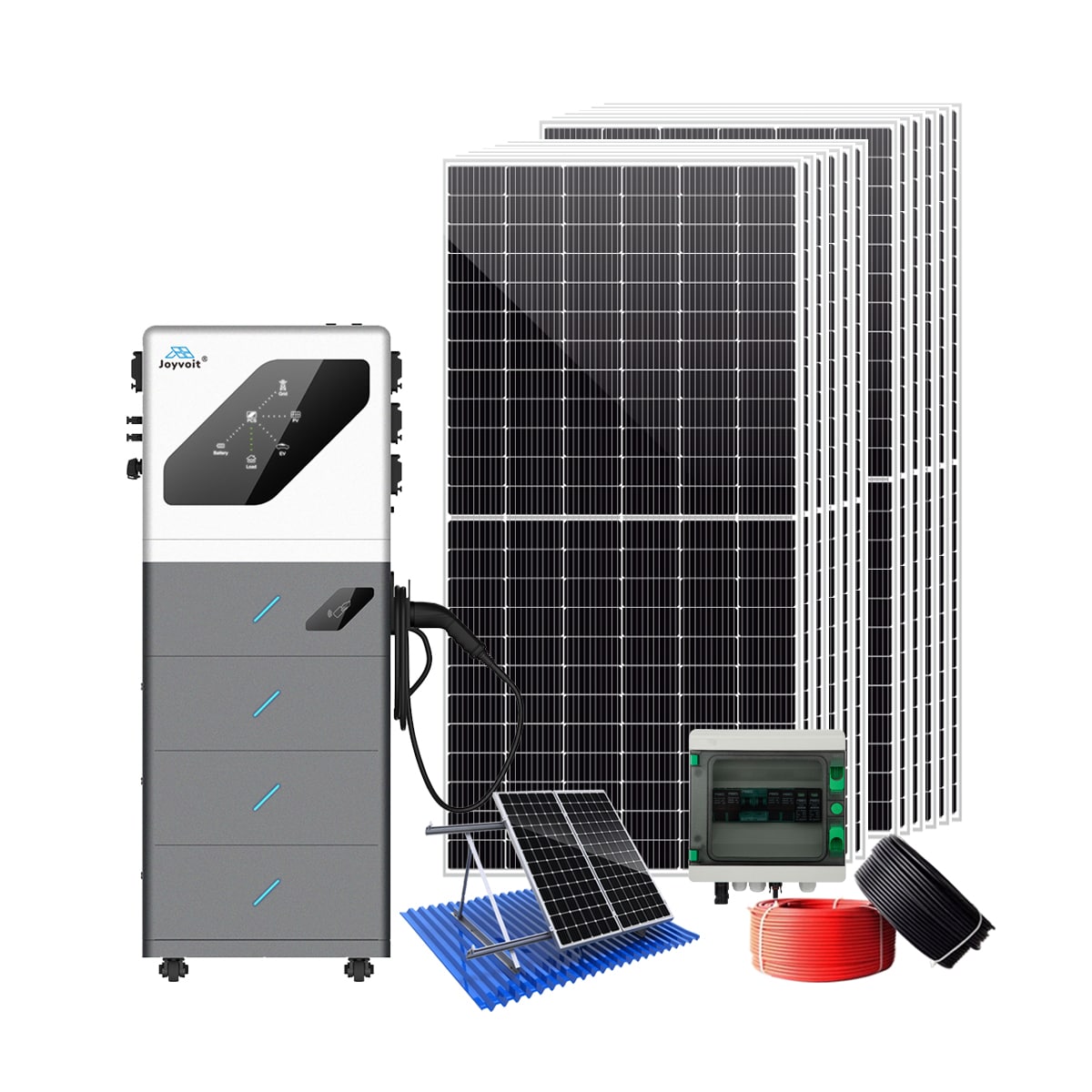
Solar EV Charger System Kits
Model: JV 10ESSC-EV7, JV 15ESSC-EV7
1.All-in-One Solution
Solar, battery storage, EV charging, power distribution
2.Easy setup, quick results
3.APP with real-time monoitor
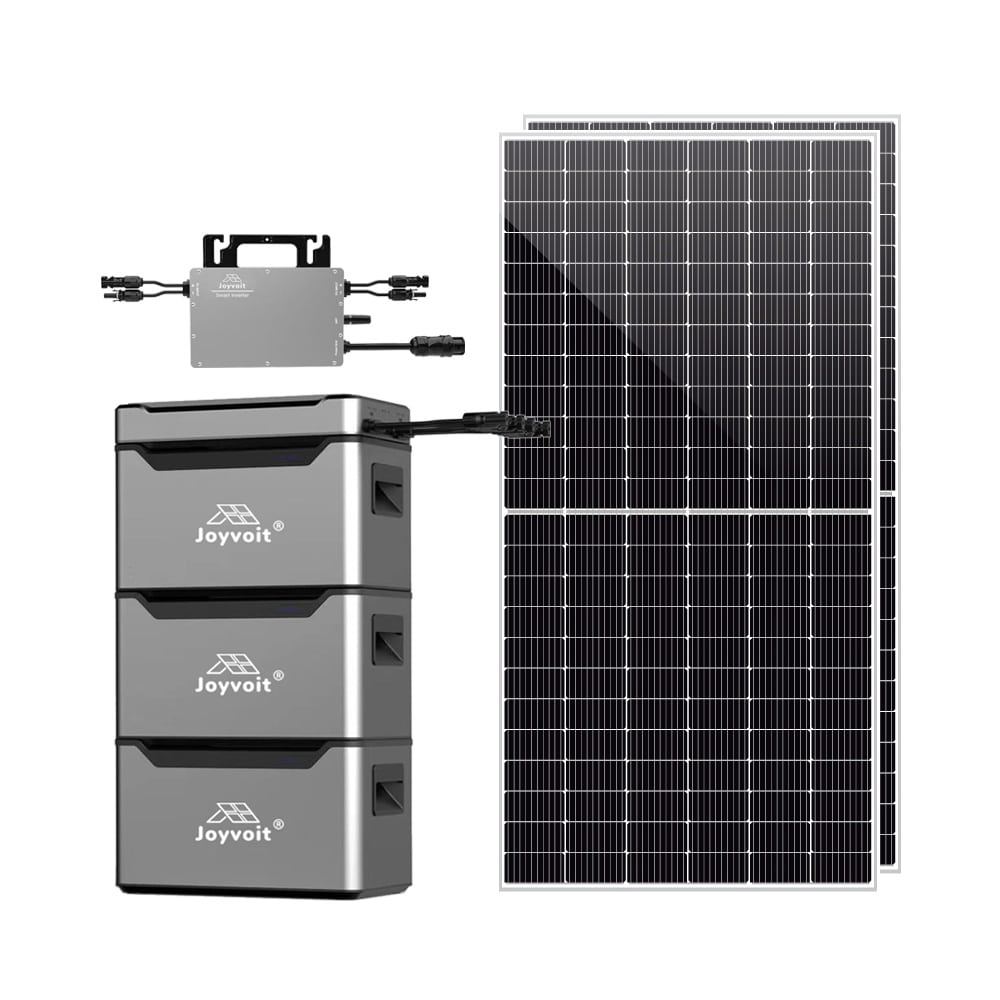
MESS Micro Energy Storage System
Model: MESS1000H
1.Versatile Solar Panel Compatibility
2.Easily Upgradable Stackable Battery
3.Seamless Integration with PVHUB
4.Adaptive Charging Modes for Optimal Efficiency
5.Monitor and Manage with Ease
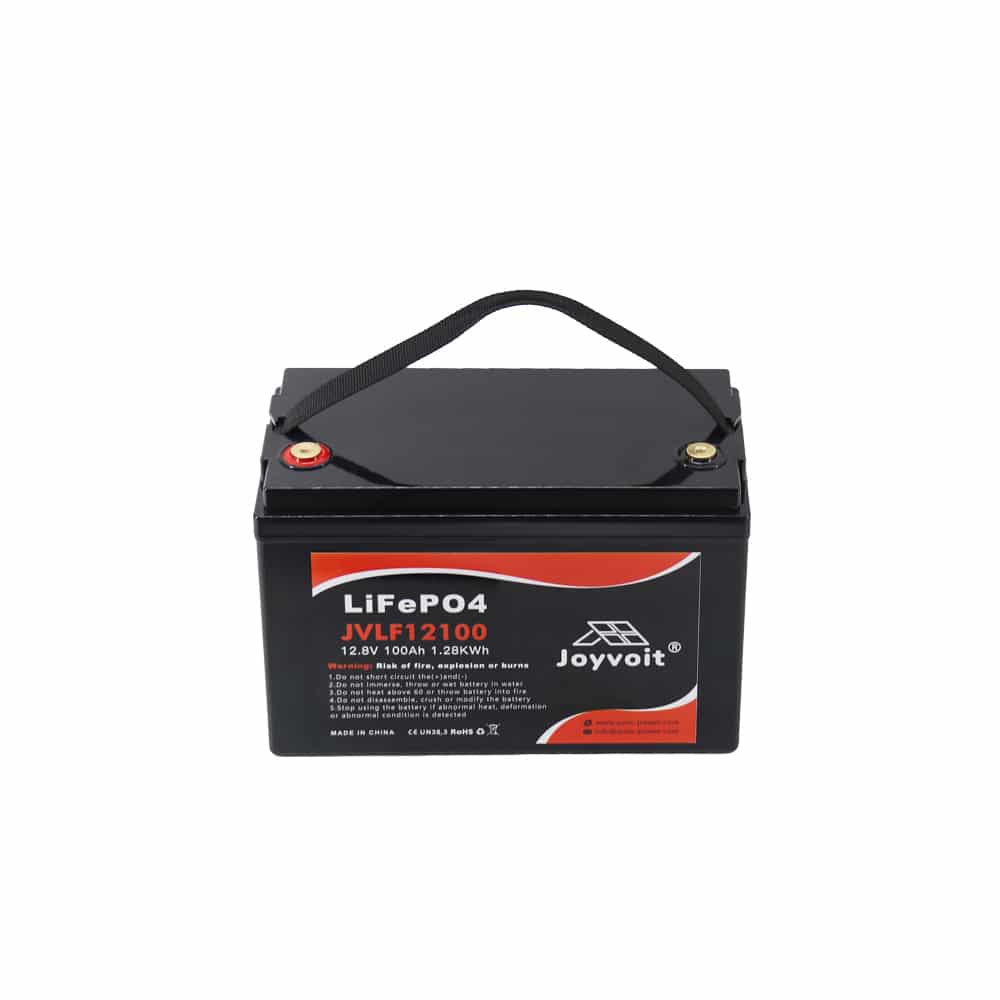
Lithium iron Phosphate Batteries Smart
Model: JVLF12100, JVLF12200, JVLF24100, JVLF2450
1.Rugged
2.Efficient
3.Size and weight
4.Bluetooth and RS485 Communications
5.Battery management system (BMS)
Join the Solar Revolution with SHENZHEN SUNS ENERGY!
Join 80,000+ customers. Explore innovative solar solutions for a greener future. Act now for a brighter tomorrow!



